This vignette demonstrates how to integrate the G-Means algorithm with the mlr3 framework for clustering. G-Means extends k-means by adapting the number of clusters based on statistical tests.
We’ll start by loading the necessary libraries:
We define a custom LearnerClustGMeans class by extending
the [mlr3cluster::LearnerClust] class for G-Means clustering.
LearnerClustGMeans <- R6::R6Class("LearnerClustGMeans",
inherit = LearnerClust,
public = list(
initialize = function() {
param_set <- ps(
k_init = p_int(2L, default = 2L, tags = "train"),
k_max = p_int(2L, default = 10L, tags = "train"),
level = p_dbl(0, 1, default = 0.05, tags = "train"),
iter.max = p_int(1L, default = 10L, tags = "train"),
algorithm = p_fct(
levels = c("Hartigan-Wong", "Lloyd", "Forgy", "MacQueen"),
default = "Hartigan-Wong",
tags = "train"
),
trace = p_lgl(default = FALSE, tags = "train")
)
super$initialize(
id = "clust.gmeans",
feature_types = c("logical", "integer", "numeric"),
predict_types = "partition",
param_set = param_set,
properties = c("partitional", "exclusive", "complete"),
packages = "gmeans",
man = "mlr3cluster::mlr_learners_clust.gmeans",
label = "G-Means"
)
}
),
private = list(
.train = function(task) {
pv <- self$param_set$get_values(tags = "train")
m <- invoke(gmeans::gmeans, x = task$data(), .args = pv)
if (self$save_assignments) {
self$assignments <- m$cluster
}
m
},
.predict = function(task) {
partition <- invoke(predict, self$model,
newdata = task$data(), type = "class_ids"
)
PredictionClust$new(task = task, partition = partition)
}
)
)
mlr_learners$add("clust.gmeans", LearnerClustGMeans)We create a clustering task using the usarrests dataset
and train the G-Means learner.
task <- tsk("usarrests")
learner <- lrn("clust.gmeans")
learner$train(task)
prediction <- learner$predict(task = task)
prediction
#>
#> ── <PredictionClust> for 50 observations: ──────────────────────────────────────
#> row_ids partition
#> 1 2
#> 2 2
#> 3 2
#> --- ---
#> 48 1
#> 49 1
#> 50 1We use autoplot() to visualize the clusters produced by
the G-Means learner. This provides a simple scatter plot of the cluster
assignments.
autoplot(prediction, task)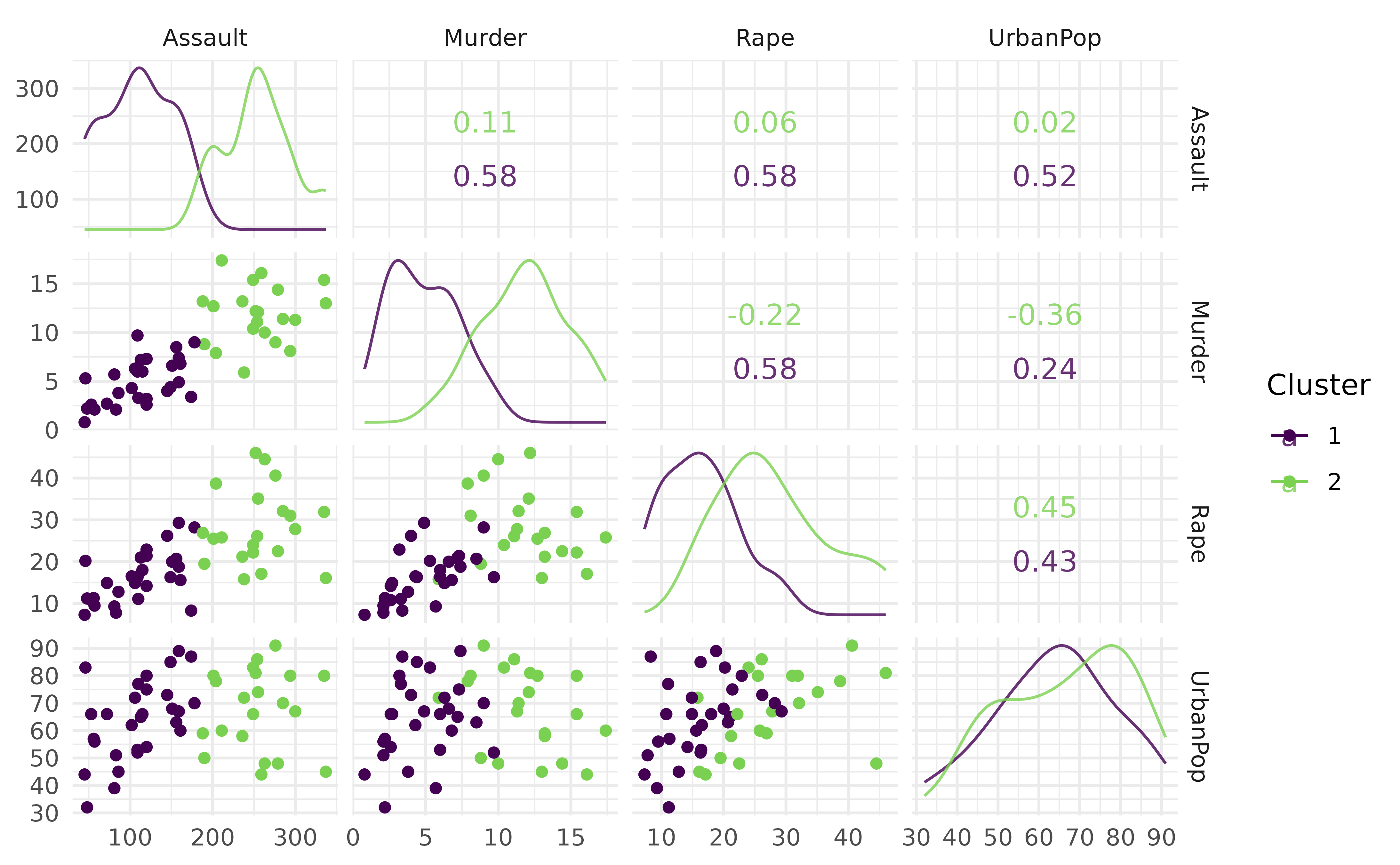
We calculate performance metrics such as within-cluster sum of
squares (clust.wss) and silhouette width
(clust.silhouette), which measure cluster compactness and
separation, respectively.
measures <- msrs(c("clust.wss", "clust.silhouette"))
#> Superclass MeasureClust has cloneable=FALSE, but subclass MeasureClustFPC has cloneable=TRUE. A subclass cannot be cloneable when its superclass is not cloneable, so cloning will be disabled for MeasureClustFPC.
#> Superclass MeasureClust has cloneable=FALSE, but subclass MeasureClustSil has cloneable=TRUE. A subclass cannot be cloneable when its superclass is not cloneable, so cloning will be disabled for MeasureClustSil.
prediction$score(measures, task)
#> clust.wss clust.silhouette
#> 9.639903e+04 5.926554e-01Alternatively, evaluate the clustering with PCA (Principal Component Analysis) and Silhouette plots:
autoplot(prediction, task, type = "pca")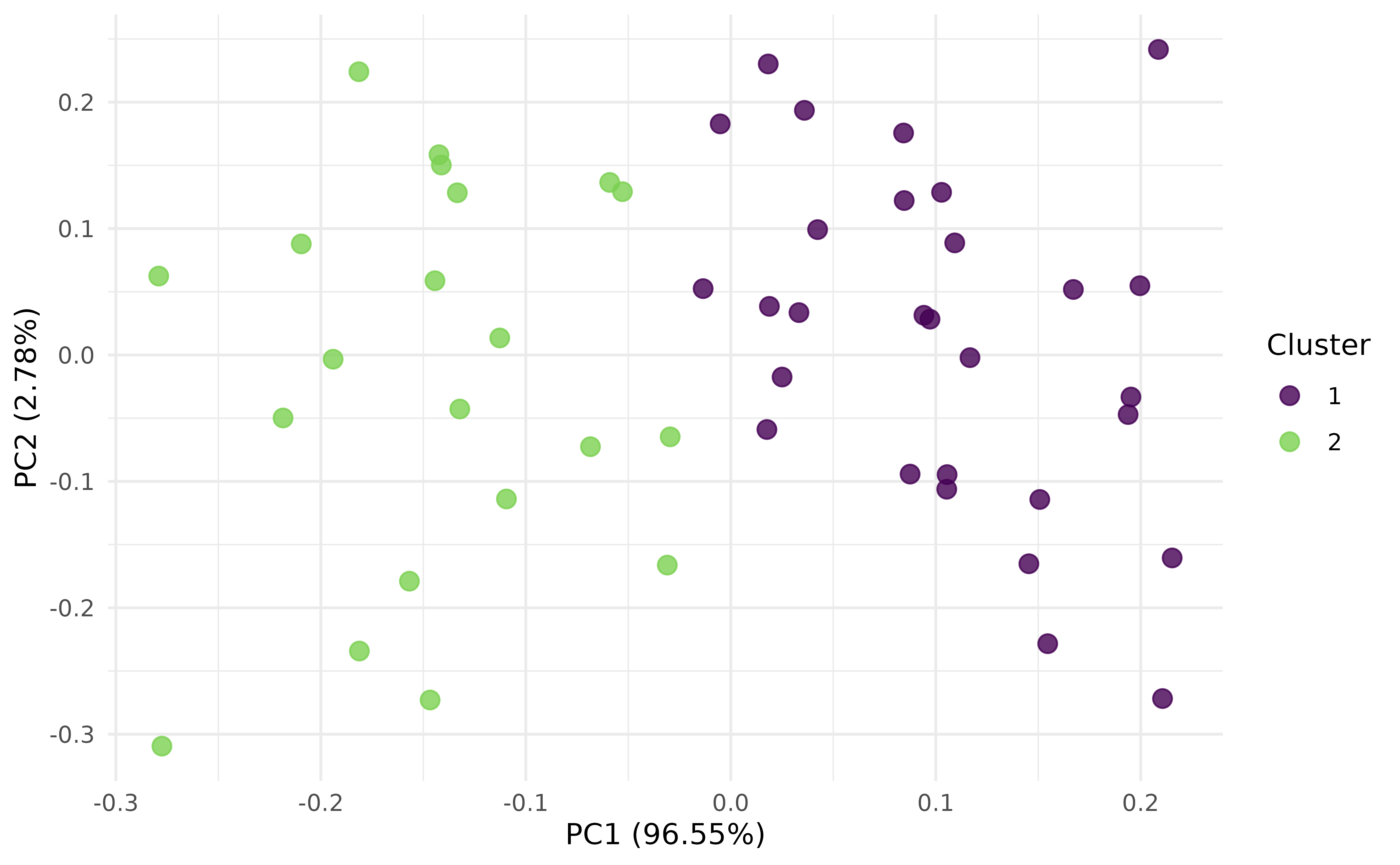
autoplot(prediction, task, type = "sil")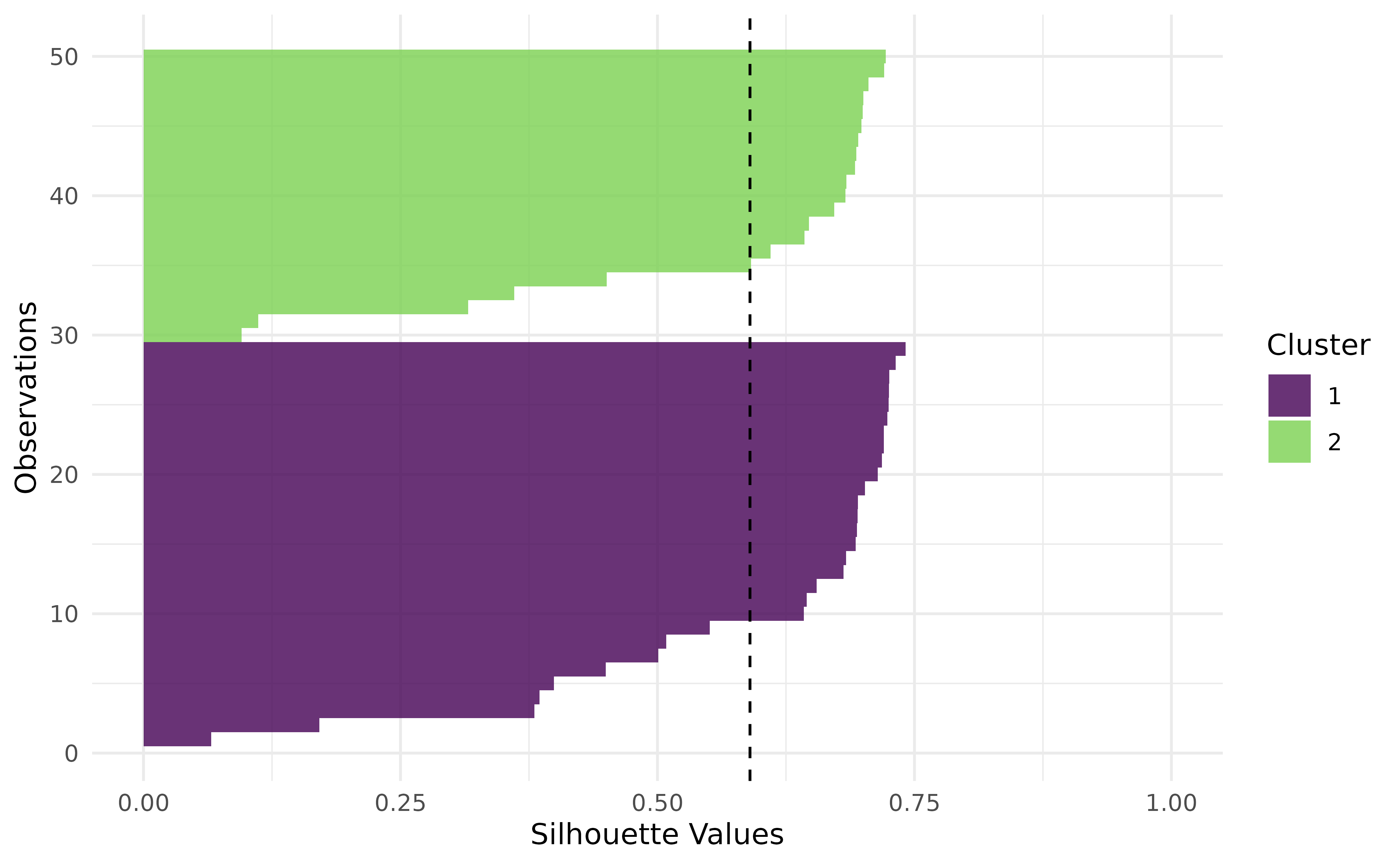
Lastly, we can now easily run a benchmark experiment to compare G-Means with other clustering algorithms.
learners <- list(
lrn("clust.featureless"),
lrn("clust.kmeans"),
lrn("clust.gmeans")
)
measures <- list(msr("clust.wss"), msr("clust.silhouette"))
#> Superclass MeasureClust has cloneable=FALSE, but subclass MeasureClustFPC has cloneable=TRUE. A subclass cannot be cloneable when its superclass is not cloneable, so cloning will be disabled for MeasureClustFPC.
#> Superclass MeasureClust has cloneable=FALSE, but subclass MeasureClustSil has cloneable=TRUE. A subclass cannot be cloneable when its superclass is not cloneable, so cloning will be disabled for MeasureClustSil.
bmr <- benchmark(benchmark_grid(tsk("ruspini"), learners, rsmp("insample")))
bmr$aggregate(measures)[, c(4, 7, 8)]
#> learner_id clust.wss clust.silhouette
#> <char> <num> <num>
#> 1: clust.featureless 244373.867 0.0000000
#> 2: clust.kmeans 89337.832 0.5827264
#> 3: clust.gmeans 7680.413 0.5668791